Evaluation of Coatings
Evaluation of GEM PVD Coatings

Coating Advantages:
- Improvement of surface sticking
- Improvement of surface hardness (up to max: 5000HV)
- Improvement of erosion resistance
- Decrease of friction coefficient (min: 0.05)
- Increase of temperature resistance (up to 1200°C)
- Improvement of surface roughness (up to Ra: 0.05)
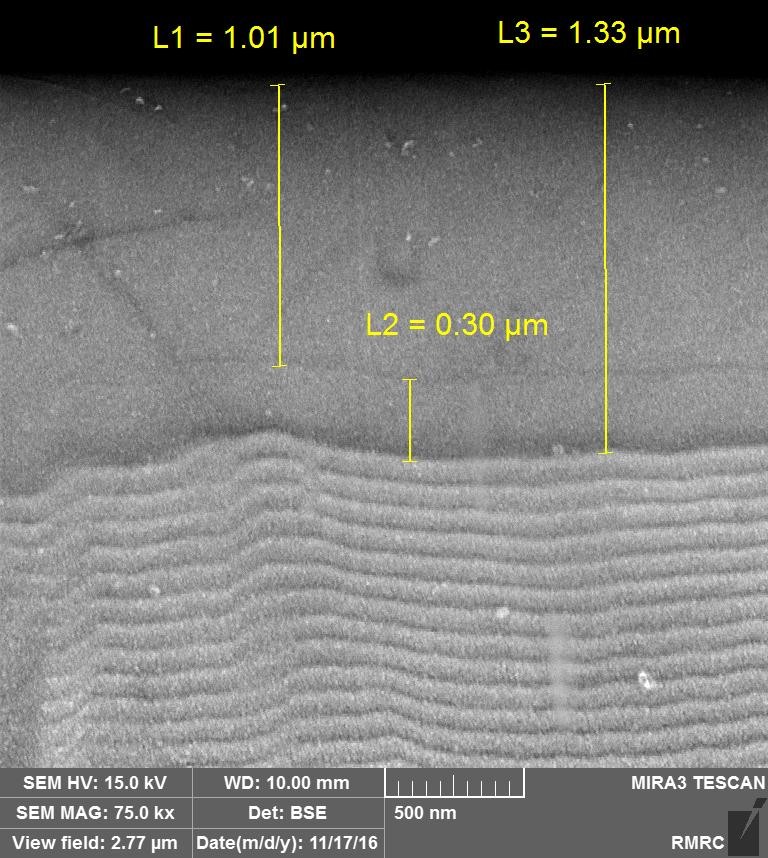
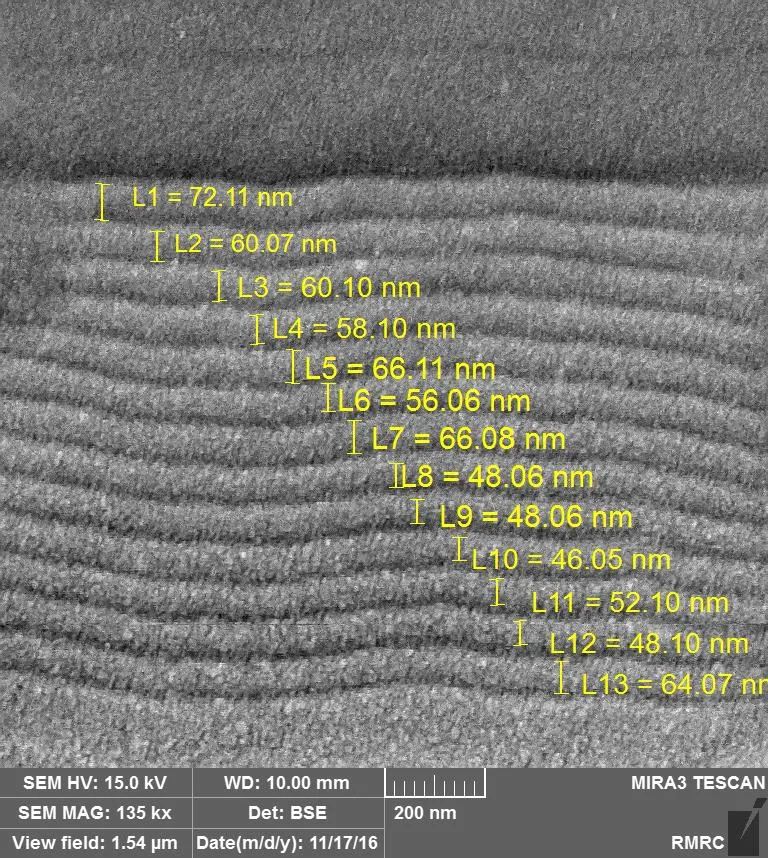
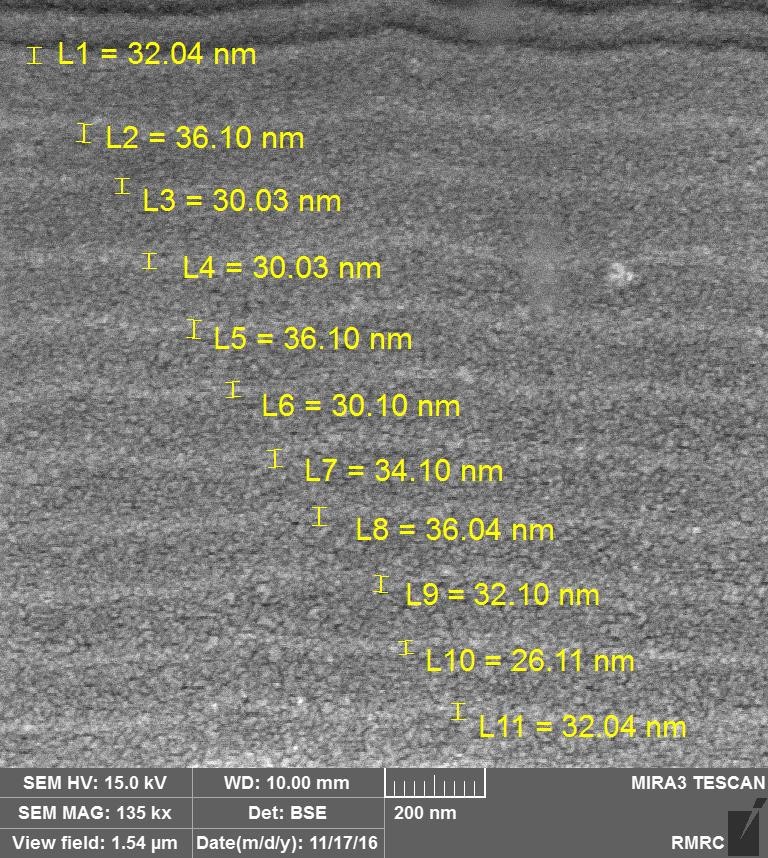
Architecture of GEM coatings
Quad nanostructure
- Substrate: HSS-8%Co
- Part “D” :TiN adhesion layer
- Part “C” :TiN-CrN hard&tough durable layer
- Part “B” :TiN-TiAlN hard&tough durable layer
- Part “A” :TiSiCN super hard top layer
- Temp. resistance:800 ⁰C
- Total thickness:4 microns
- Roughness(Ra):0.15 µm
- Total hardness:34 GPa
- Excellent wear resistance
GEM Nano-Coating Evaluation in major industrial applications:
1-High speed round cutting tools include: Drills, Taps, Reamers, End mills, saws
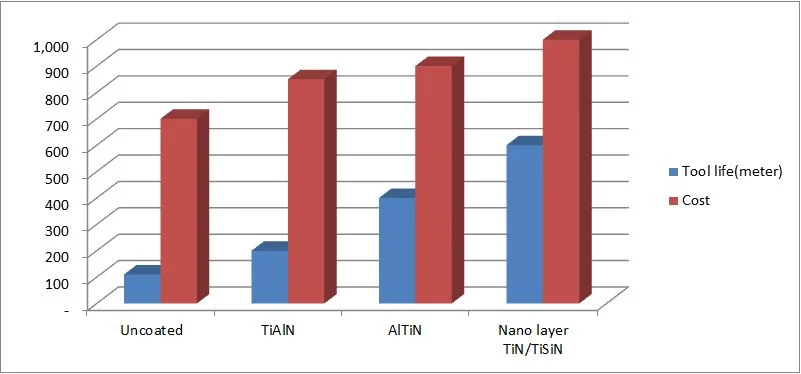
The coating type is depends on the kind of work piece. Tool life increase 2-5 times more (depend on coating type, application condition and substrate type)

Substrate: SAW
Precision cutting of 3 mm profiles, Cast Iron
Tool: carbide circular saw blade ɸ 100mm x 0,8mm, z=200
Cutting conditions: n=400 rev/min, vf=64 mm/min, lubrication: oil
Source: Iran industrial valves/Isfahan/Iran

Substrate: End mill
Work piece material: X40CrMoV5 – 1.2344 – R =1100 N/mm²
Tools: d=12mm – solid carbide end mill with corner radius r=2mm
v = 218 m/min – f=0.26mm – a =0.5mm – a =8mm – emulsion 7%
Source: Abzar sanat co./Tehran/Iran

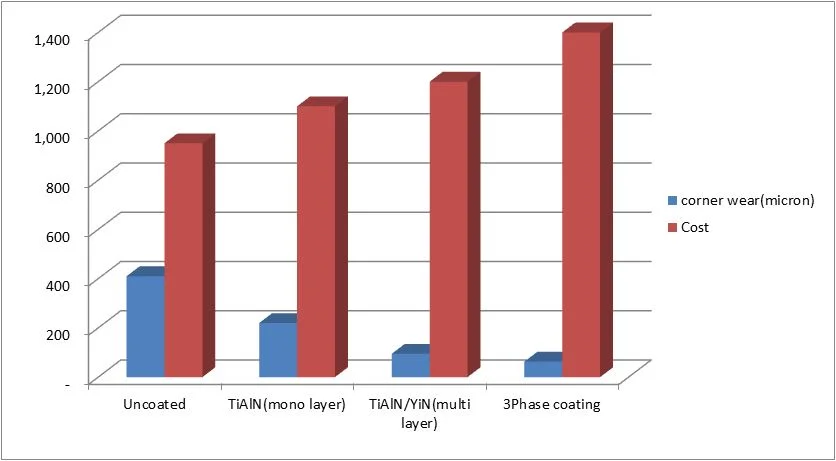
Substrate: Drill
Material: 42CrMo4 – IC-p=40 bar – emulsion 5% –
Comparison after L =50m drilling distance
Tools: solid carbide drills – d=12mm a =5xd-v=120 m/min-f=0.35 mm/rev
Source: Vamco co./Tehran/ Iran

2-Punching and deep drawing and forming dies:
The coating type is depend on application condition and substrate type. Tool life increase 2-20 times more
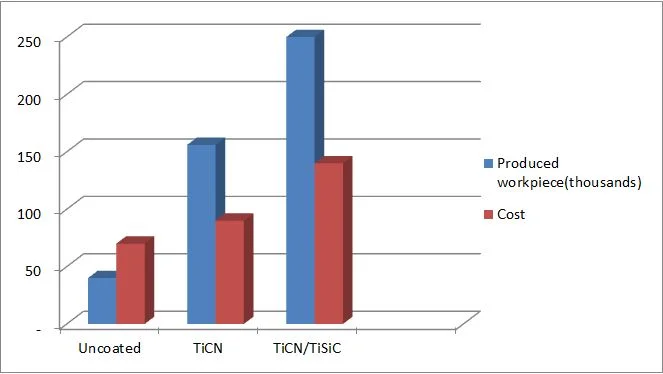
Substrate: Punch
Punch material: Hss-8%Co, Hardness: 64 HRC
Work piece material: INOX 0.8 mm;
Source: Poolad tarash Iran co./Isfahan/Iran

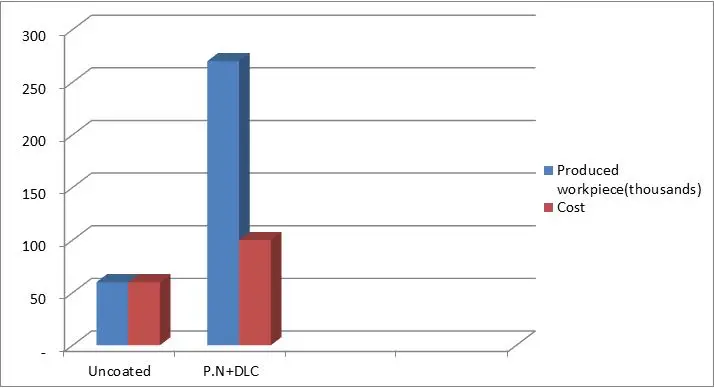
Substrate: Deep drawing Die
Material of die: 1.2379,58 HRC
P.N Thickness: 150micron,
Work piece material: ck45
Source: Part Lastic co./Mashhad/Iran

3-Hob & shaper gear cutter:
The coating type is depend on speed of cutting and work piece material) Tool life increase 5-30 times more (more tool life increase for re-sharpened tools)

Substrate: Gear SHAPER
– Steel 27MnCr5 (270HB), Modulus2
– Substrate: S290 (1010HV10)
Cutting conditions: Vc = 140 m/min,
Hmax=0.3mm, dry, down Shaping
Source: Niroo Mohareke co./Ghazvin/Iran

4-Die casting
The coating cause: more delay for thin cracks, no sticking of aluminum to die, Better temperature resistance of die, low coat work piece production. Working time until failure (days)

Substrate: Die casting Pins
Substrate material: 1.2344, 48HRC
P.N. Thickness: 100Micron
PVD Thickness: 5Micron
Source: Iran Khodro casting co./Abhar/Iran

5-Hot forging of brass
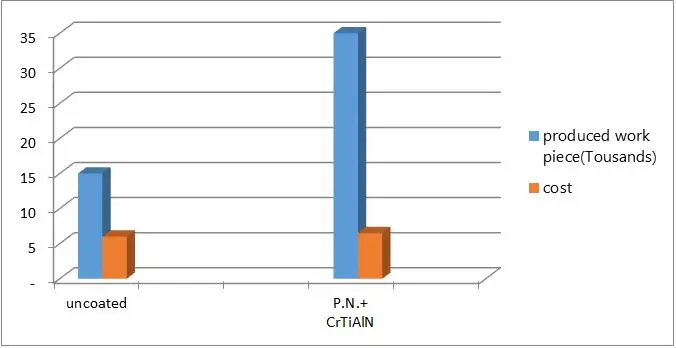
Substrate: Hot forging Die
Die material: 1.2344, 48HRC
Work piece temperature: 760°C
P.N, Thickness: 100 micron, PVD Thickness: 7micron
Source: Azaran co./Isfahan/Iran

6-Hot forging of steel
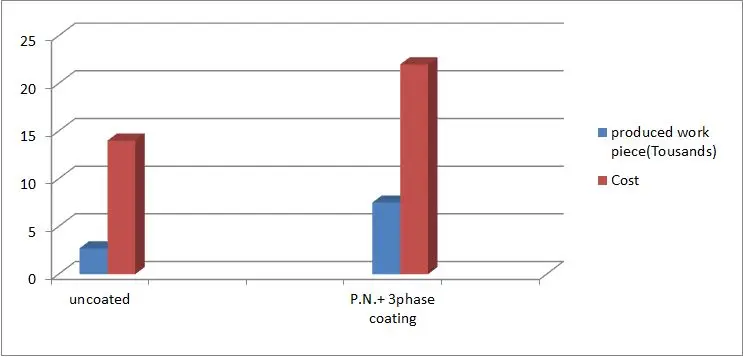
Substrate: Hot forging Die
Die material: 1.2344, 48HRC
Work piece temperature: 1100°C, Press force: 1100 tons
P.N, Thickness: 150 Micron, PVD Thickness: 7 micron
Source: Mashhad forging co./Mashhad/Iran